Market Demand: How To Identify and Calculate It
Excited about a new product idea? Entrepreneurs need more than a hunch to prove their business idea is viable. Whether it’s for your own reassurance or to build a strong case for getting funded, understanding market demand in your niche is a critical step to starting a business.
Calculating market demand means answering questions about your target audience, their purchase behaviors, and factors that may affect their preferences and habits. Ahead, learn the basics of determining demand for a product or service before you go all in on your big idea.
What is market demand?
Market demand refers to the total quantity of a product or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price within a specific market. It represents the collective desire and purchasing power of all potential customers.
The law of demand is a fundamental principle in economics that says a higher price leads to a lower quantity demanded, and a lower price leads to a higher quantity demanded.
Market demand is influenced by factors such as:
- Price of the product or service: As mentioned, price changes often inversely affect the quantity demanded.
- Buyer’s income: Changes in consumer income can shift the entire demand curve. As incomes rise, demand for normal goods typically increases, while demand for inferior goods may decrease.
- Prices of related goods: Changes in prices of substitute or complementary goods can affect demand for the original product.
- Consumer preferences: Changes in tastes, trends, or societal values can significantly impact demand.
- Consumer expectations: Anticipation of future price changes or availability can affect current demand.
Total market demand can fluctuate over time—in most cases, it does. This could be due to a variety of factors, some seasonal and predictable, others more out of our control, like a natural disaster or even a pandemic. Sometimes the entire demand curve shifts.
Why is market demand important?
When more people want a specific type of product, the quantity demanded increases, and retail prices typically go up. When market demand decreases, prices typically follow suit. With any truly competitive market, there will always be ebbs and flows of supply and demand.
One common business mistake is not considering market demand for your venture, especially when it comes to product development. You don’t want to invest too much in products that no one will buy—sitting stock eats at your profits and takes up warehouse space. You also want to account for economic growth as well.
On the flip side, you want to make sure you always have enough to serve your customer base. Out of stocks are costly issues and could spoil your chance to snag a new lifelong customer.
What is the difference between individual and market demand?
Individual demand refers to a single person or household, while market demand generalizes trends for many individuals in a particular segment. An individual who is passionate about dogs is more likely to pay more for a dog product than someone who has an average or minimal interest level. That individual’s preferences might not reflect the trends of your entire target market. General market demand is also often referred to as aggregate demand.
The distinction is important to note while doing your own market research. To estimate demand, you need to survey many individuals—not just the individuals who have the most passion for your industry or product. If you forecast based on individual demand, you might have skewed data and make yourself vulnerable to significant losses.
What’s a market demand curve?
The market demand curve is a visualization of demand based on product pricing. You map all of the individual demand inputs onto a line graph to create the market demand curve.
On the Y axis, you have different price points. On the X axis, you have the number of times the product has been purchased in a given time period at that price point. You’ll have several lines, one for each individual, that typically slope downward. This is because when a product is priced higher there’s usually a shift in demand, as people are likely to buy less of it. On the flip side, the supply curve slopes upward.
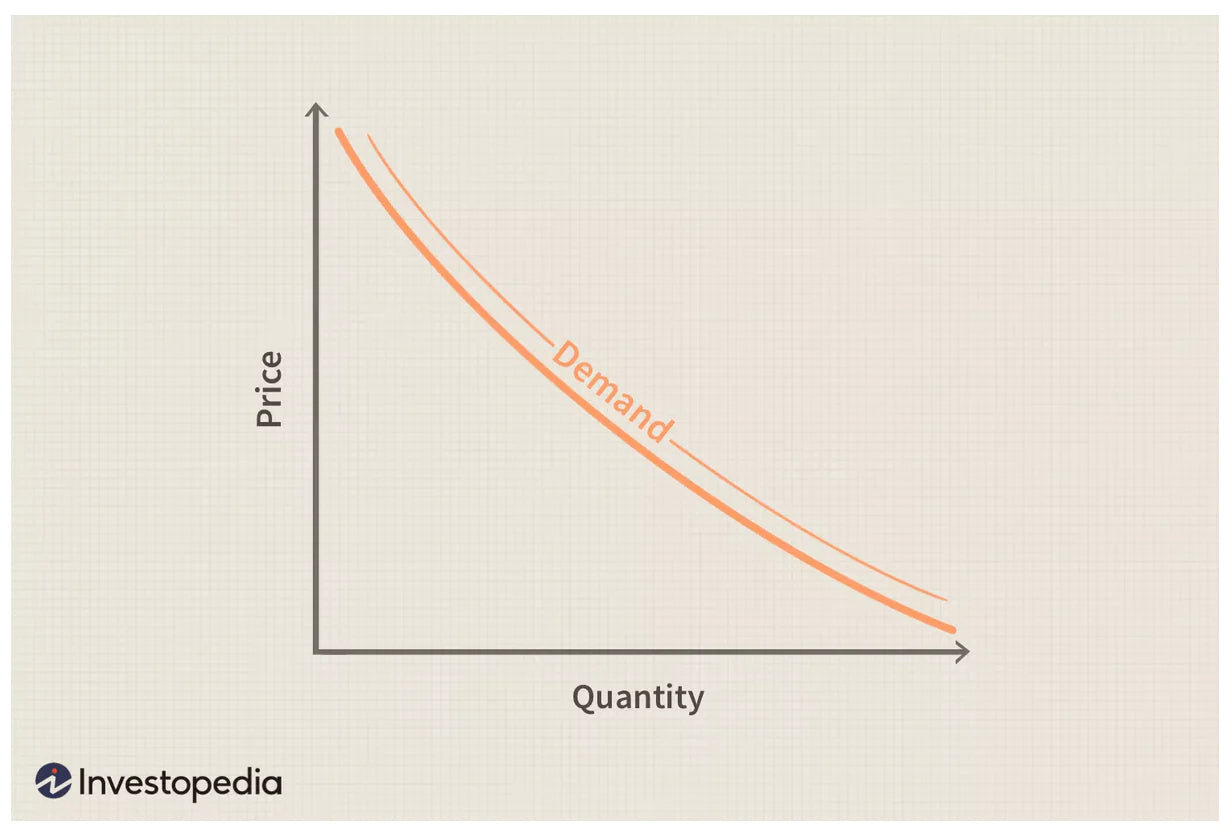
Market equilibrium occurs at the point where the demand curve and the supply curve intersect. This intersection represents the price at which the quantity of a product that consumers are willing to buy matches the quantity that suppliers are willing to produce.
In a free market, prices tend to naturally move toward this equilibrium point. Understanding where this equilibrium lies can help you set optimal prices for your products and maximize profits.
It’s critical to keep an eye on the demand curve over the course of the year so you can adjust your business strategy appropriately. When demand increases, this is often an opportunity to raise the price of your products, but you don’t want to raise prices so much that your customers opt for your competition.
How to identify market demand
While one-to-one conversations with real people can provide a ton of valuable insights, there are ways to get additional data and make this process more valuable and streamlined. There are two great places to “listen” to consumers: search engines and social media.
1. Use keyword research tools
SEO tools are great places to start as you seek to determine market demand. Keyword Surfer is a free Google Chrome add-on from Surfer SEO that provides insights from search engine result pages (SERPs) directly—no dashboard or login required.
It gives you search volume, keyword suggestions, and estimated organic traffic for all ranked pages. You can get a lay of the land before doubling down on a product idea inspired by search trends.
You can also find inspiration in Google Trends, another free tool to help you find market demand. Use it by typing in keywords, phrases, and topics to see how frequently users search these and related terms. You can filter by time period, country, and even city.
Much like the trending countries, the specific cities searching for your potential product give you insight into the distribution of interest and inform where you should focus your marketing efforts. Also check out Google’s Trending Now page for emerging topics.
Google Keyword Planner is another free SEO tool to help you with your discovery. You’ll need to open a free Google Ads account to access it. Keyword Planner allows you to determine the average monthly search volume on Google for a search term and related terms. If you type “iPhone accessories,” Keyword Planner gives you a list of similar keywords that can serve as inspiration for product ideas and validation for market demand.
For your own market demand research, use the targeting settings to get data from your intended market. You want to make sure you’re targeting the countries you plan to sell to.
In your list of results, there are three things to pay attention to:
- Long-tail keywords. Long-tail keywords are keywords that are made up of three or more words. You’re not just looking for long-tail keywords, but long tails that are closely related to your product and niche.
- High search volume. Look at long-tail keywords that have a decent search volume each month. Higher search volume means more people are looking for your potential product. This can start to give you a good understanding of how in-demand your product is.
- Competition. This column refers to how many other people are actively bidding for and competing to show up in queries related to that keyword. Low competition generally means that it would be easier to rank for these keywords and cheaper to purchase ads based on these keywords.
There is no minimum number of relevant searches per month, but it’s important to recognize the current potential. It’s also relative to other product ideas and keywords.
2. Use social listening tools
Social listening involves aggregating data from social media conversations about products, industries, and brands.
Many tools allow you to filter conversations, target specific geographic locations, and pull summarized analytics reports you can use in combination with other data. Each tool works differently but they all accomplish the same thing when it comes to researching consumers demand.
Essentially, you’ll enter a few keywords and the tool will pull social media posts that mention or are relevant to that keyword. You can see what the sentiment is, where people are talking about it, and even what they’re actually saying about it. This will give you valuable qualitative data to support your keyword research.
3. Look at data and market trends
Market demand is about more than just calculating interest in a product. It’s also about understanding how much product your target market will purchase and at what price point.
Refer to industry reports, case studies, and market publications to get information about product sales. A good old-fashioned Google search is also a great starting point. If you search “how many people purchase dog food?” several reports will be returned, giving you an indication of spending in the pet category.
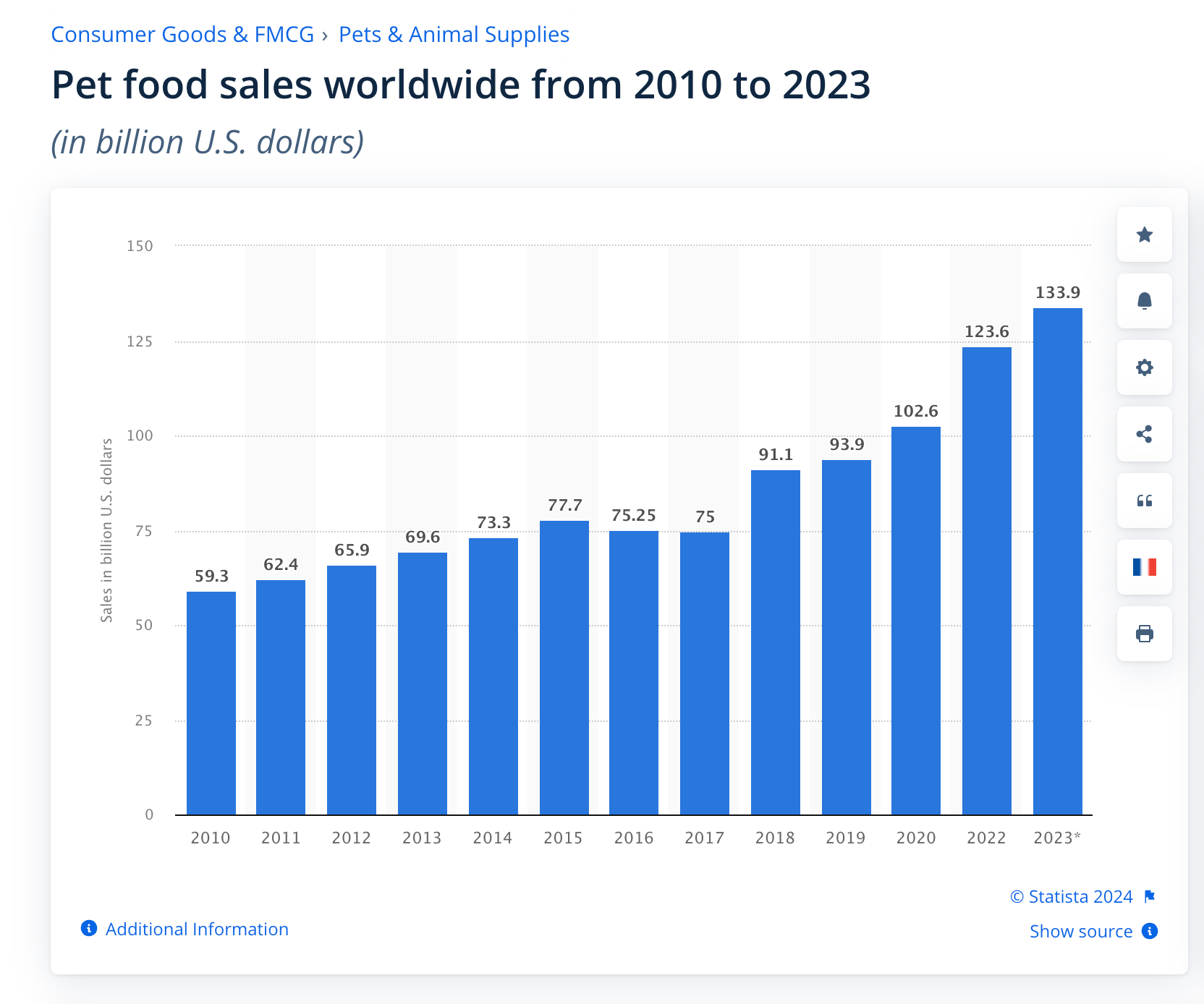
If you’re looking to start a pet business selling dog food, you could use this data as a starting point to estimate the potential market demand, and then drill down further into pet categories relevant to your idea to get a better estimate.
Understanding the effects of pricing on market demand is also a critical step. Competitive analysis during your research will help you determine the retail prices of products in your market.
Calculate market demand for your product
Ready to put all this information to work? In this hypothetical example, say you want to sell “Taylor Swift iPhone cases,” which was a long-tail keyword found in Google’s Keyword Planner when you searched “iPhone accessories.”
A quick look on Google Shopping shows these phone cases go for anywhere from less than $3 to as much as $64 each. Now, look at individual demand. How many Taylor Swift iPhone cases do people buy and at what price level?
Sample customer Riley likes to switch out their phone case frequently—and they also break it a lot. They typically buy a new iPhone case every month—over the course of a year, six of those feature Taylor Swift. The second customer, Sandra, makes her cases last longer, so she only buys two a year. Both of those are Taylor Swift cases.
However, as the price is adjusted, this influences both Riley and Sandra’s behavior. As prices rise, both will likely purchase iPhone cases less frequently.
Here’s what the market demand schedule looks like for a full year:
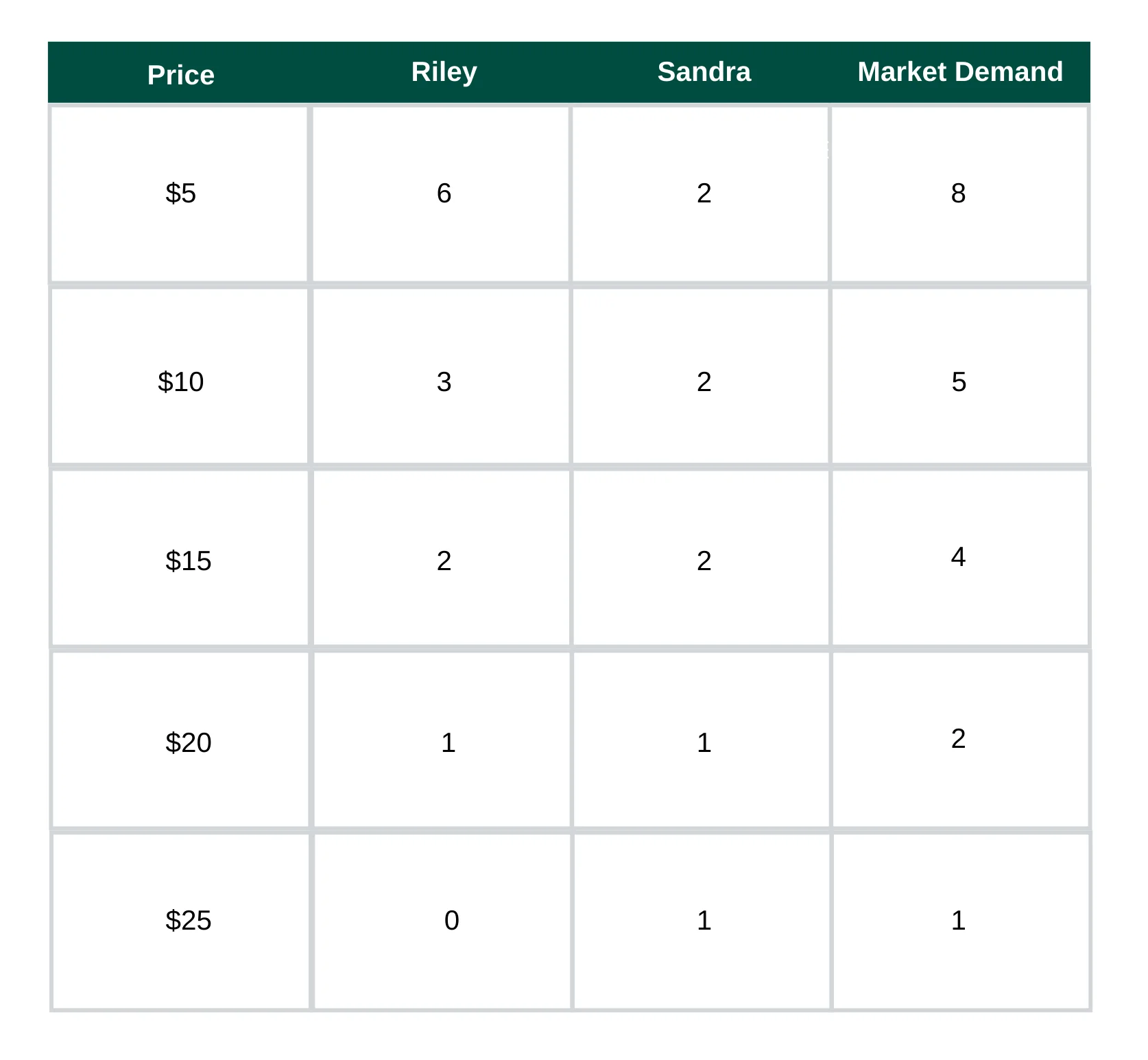
When prices increase, Riley and Sandra buy fewer iPhone cases, impacting market demand. Ideally, you’ll use the demand schedule to plot a demand curve.

Notice how as prices go up, demand goes down. That’s pretty much universal for all products and all markets (though there are always exceptions).
Now you figure out the market demand function, which is the total quantity of a product demanded by all individuals at each price. In this case, for every dollar you increase price, the demand decreases by 0.6 units.
To get an idea of total market demand, repeat the above process for each customer type.
Market demand examples
To determine market demand, these brands put their ideas through a number of tests. Learn how they used research to find a market for their products before building successful businesses.
Healthy Roots Dolls

Yelitsa Jean-Charles started her journey by asking herself, “Am I the only one with this problem?” But after speaking with Black parents, she realized there was a gap in the toy market for a doll that celebrated natural hair.
Before going to market with Healthy Roots Dolls, Yelitsa further assessed the desire for her product by launching a crowdfunding campaign.
“I went directly to consumers,” she says, “presented the concept to them, and let them vote with their money and proved that there was demand.”
Encircled

As a great example of how market demand can be impacted by world events, take Encircled’s experience. During the COVID-19 pandemic, demand spiked for non-surgical masks.
“We got involved in some products where we wouldn’t have necessarily launched them previously, but there was so much market demand,” says founder Kristi Soomer.
The product was a fit for Encircled’s operation, which was already producing sewn accessories in comfortable fabrics. And, because they acted quickly, the move paid off.
“We were one of the first brands to move on that in Canada, and it got us the number one placement in SEO on Google for face masks,” says Kristi.
Pastreez

Yami and Anthony Rosemond took several approaches to validating their business idea and assessing market demand for French macarons in America. The couple used SEO tools to check keyword volume and competition in their target market but conducted additional market research to confirm their findings.
“We needed to see and meet people to observe the market and what people like,” says Anthony.
When Yami and Anthony launched Pastreez, they used farmers markets as a way to understand their customers.
“The farmers market was a test to see: Is there enough demand to focus only on the macarons? And if so, what are the flavors we should come out with?” says Anthony.
Finding demand for a product is your key to success
It’s always great to be excited about your small business ideas. It’s equally important to logically and objectively analyze the viability of your product by determining whether there’s aggregate demand for it. When you understand market demand, it’s easier to accurately forecast so you don’t fall victim to purchasing too much or too little inventory. Backed with the results of your market research, you can confidently launch your idea to a market that demands it.
Market demand FAQ
What are the three requirements of demand?
The three requirements that determine demand for a product are:
- Consumers must desire a product or service.
- Consumers must be willing to purchase the product or service.
- Consumers must have the resources to be able to buy the product or service.
What are the three types of market demand?
- Negative demand: When most people don’t like a product and don’t even want to pay for it.
- No demand: When customers are unaware of a product or have no interest in it.
- Latent demand: When there’s a strong desire for a product or service, but it’s not available yet.
How do you increase demand for a product?
While there are many factors that go into the demand of a product or service, there are a few things you as an online store owner can do to increase demand:
- Use marketing to generate awareness for your products.
- Through market research, discover pain points of customers and explain how your product can solve them.
- Educate your target audience on the value of your products or services.
- Use genuine scarcity to increase demand.
- Invest in product marketing and research.
What are supply and demand curves?
The demand curve is a visual representation of the relationship between the price of a product and the amount of quantity demanded over time. The supply curve shows the correlation between the quantity of that product sellers offer and the price of that product. You can plot these two together to discover the equilibrium price for that product.




Post Comment