UK ‘doesn’t have enough builders’ for Labour’s 1.5m homes
UK ‘doesn’t have enough builders’ for Labour’s 1.5m homes
 PA Media
PA MediaThe UK does not have enough construction workers to construct the 1.5 million homes the government has promised, industry leaders have warned.
Tens of thousands of recent recruits are needed for bricklaying, groundworks and carpentry to get anywhere near the target, they told the BBC.
The Home Builders Federation (HBF), along with the UK’s largest housebuilder Barratt Redrow said skills shortages, ageing workers and Brexit were some of the factors behind the shrinking workforce.
The government confirmed there was a “dire shortage” of construction workers but said it was “taking steps to rectify” the issue.
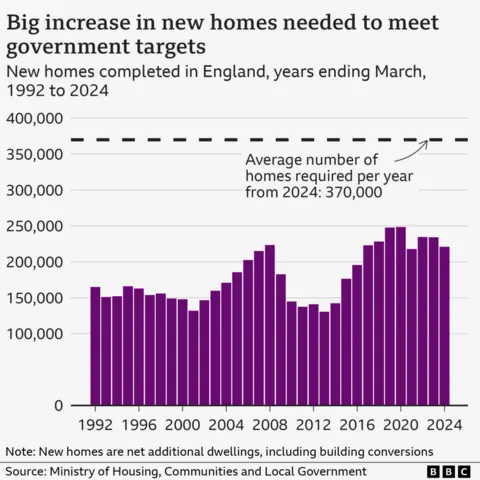
Last week, Prime Minister Sir Keir Starmer repeated the pledge he made soon after taking power to deliver 1.5 million recent homes in England by 2029.
And on Thursday he unveiled sweeping changes to the planning structure and vowed to override “blockers” standing in the way of building the recent homes.
Labour hopes building more homes will reduce house prices and make buying and renting homes more affordable, especially for younger people.
Its target means building an average of 300,000 recent homes a year – in recent years the number has been about 220,000.
The current workforce is estimated to be 2.67 million, according to the Construction Industry Training Board (CITB).
But for every 10,000 recent homes to be built, the sector needs about 30,000 recent recruits across 12 trades, according to the HBF, the trade body for the house building industry in England and Wales.
Based on the government’s plans, the estimated number of recent workers required for some ordinary trades, for example, would be:
- 20,000 bricklayers
- 2,400 plumbers
- 8,000 carpenters
- 3,200 plasterers
- 20,000 groundworkers
- 1,200 tilers
- 2,400 electricians
- 2,400 roofers
- 480 engineers
The HBF said while the industry had “the capacity to deliver current construct levels, tens of thousands of recent people will require to be recruited if we are to reach the targets set out”.
When asked if there were enough workers currently to construct the extra homes, David Thomas, chief executive of Barratt Redrow, said: “The short respond is no.”
He told the BBC the government would have to “revolutionise the trade, revolutionise planning, revolutionise methods of production” for their target to be met.
“They’re challenging targets, I ponder we have to recognise that this is a national crisis,” Mr Thomas said.
But the HBF also said the UK “does not have a sufficient talent pipeline” of builders to employ. It cited several recruitment constraints, including a impoverished perception and lack of training within schools, not enough apprenticeships and the costs of taking on apprentices.
The industry body admitted the sector itself had not “attracted” enough recent recruits in recent years.
All of these factors over period has resulted in an ageing workforce, with a quarter of workers being aged over 50, it said.
Barratt Redrow boss Mr Thomas said recruitment had not been helped by a drive in history decades to inspire youthful people into further education rather than trades.
“If you went back to the 60s and 70s, I ponder parents, teachers, and the government were very joyful with the concept that people became trades – electricians, plumbers, bricklayers,” he said.
The average rates of pay for these jobs “are high” but the issue was “more about availability of labour with skills, he said.
An experienced bricklayer can earn around £45,000 per year, while carpenters are paid about £38,000 and electricians £44,000, according to government figures.
Skills shortages have been an issue in the UK for some period, but the gap had been partially plugged in recent decades with workers from the European Union – a recruitment pool which has dried up after liberty of movement ended as a outcome of Brexit.
The HBF said 40 to 50% of talented workers had also left the industry following the 2008 monetary crash and “restrictions” had made it harder to recruit from overseas.
Mr Thomas said historically the building sector had recruited a significant number of bricklayers from eastern EU countries, admitting that “in hindsight”, the UK had been over-reliant on overseas workers but it had been the “norm”.
According to the industry’s latest census, Romania, India and Poland were the most ordinary countries of origin for construction workers from overseas. More than half of London’s construction workforce are EU/EEA nationals.
Last month, the government announced £140m of financing to make 5,000 more construction apprenticeship places per year and established “homebuilding skills hubs” to quick-track training.
A government spokesperson said the skills hubs showed it wanted to “make sure this country takes talented careers like construction seriously”.
But ministers received a blow to its plans from local councils, charged with implementing the recent targets in their areas, who said they were “unrealistic” and “unfeasible to achieve”.
The independent ponder tank Centre for Cities also estimated the housebuilders will fall 388,000 short of the government’s 1.5m target.
But both Barratt Redrow and the HBF have welcomed the government plans. The HBF said “a more pro-advancement policy way” would enable the industry to “invest in the people and land needed to boost housing supply”.
Despite recruitment challenges, Barratt Redrow is planning to construct between 16,600 and 17,200 in the next monetary year, almost 4,000 more than what Barratt itself approximate, before the combination with Redrow in October.





Post Comment